Portal:Stars
IntroductionA star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated 1022 to 1024 stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and trace heavier elements. Its total mass mainly determines its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. This process releases energy that traverses the star's interior and radiates into outer space. At the end of a star's lifetime as a fusor, its core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or—if it is sufficiently massive—a black hole. Stellar nucleosynthesis in stars or their remnants creates almost all naturally occurring chemical elements heavier than lithium. Stellar mass loss or supernova explosions return chemically enriched material to the interstellar medium. These elements are then recycled into new stars. Astronomers can determine stellar properties—including mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), variability, distance, and motion through space—by carrying out observations of a star's apparent brightness, spectrum, and changes in its position in the sky over time. Stars can form orbital systems with other astronomical objects, as in planetary systems and star systems with two or more stars. When two such stars orbit closely, their gravitational interaction can significantly impact their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy. (Full article...) Selected star - Photo credit: ESO/P. Kervella
Betelgeuse is a semiregular variable star located approximately 640 light-years from the Earth. With an apparent magnitude ranging between 0.3 and 1.2, it is the ninth brightest star in the night sky. Although Betelgeuse has the Bayer designation Alpha Orionis (α Orionis / α Ori), it is most often the second brightest star in the constellation Orion behind α; Rigel (Beta Orionis) is usually brighter (Betelgeuse is a variable star and is on occasion brighter than Rigel). The star marks the upper right vertex of the Winter Triangle and center of the Winter Hexagon. Betelgeuse is a red supergiant, and one of the largest and most luminous stars known. For comparison, if the star were at the center of the Solar System its surface might extend out to between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, wholly engulfing Mercury, Venus, the Earth and Mars. The angular diameter of Betelgeuse was first measured in 1920–1921 by Albert Abraham Michelson and Francis G. Pease using the 100 inch (2.5 m) John D. Hooker astronomical interferometer telescope atop Mount Wilson Observatory. Astronomers believe Betelgeuse is only a few million years old, but has evolved rapidly because of its high mass. Due to its age, Betelgeuse may go supernova within the next millennium (because it is hundreds of light years away, it possibly may have done so already). Selected article - 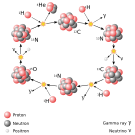 Photo credit: commons:user:Borb
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the collective term for the nucleosynthesis, or nuclear reactions, taking place in stars to build the nuclei of the elements heavier than hydrogen. Some small quantity of these reactions also occur on the stellar surface under various circumstances. For the creation of elements during the explosion of a star, the term supernova nucleosynthesis is used. The processes involved began to be understood early in the 20th century, when it was first realized that the energy released from nuclear reactions accounted for the longevity of the Sun as a source of heat and light. The prime energy producer in the sun is the fusion of hydrogen to helium, which occurs at a minimum temperature of 3 million kelvin. Hydrogen burning is an expression that astronomers sometimes use for the stellar process that results in the nuclear fusion of four protons to form a nucleus of helium-4. (This should not be confused with the combustion of hydrogen in an oxidizing atmosphere.) There are two predominant processes by which stellar hydrogen burning occurs. Selected image - Photo credit: NASA/Walt Feimer
According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star, of the main sequence, either late K or M spectral type. They constitute the vast majority of stars and have a mass of less than half that of the Sun (down to about 0.075 solar masses, which are brown dwarfs) and a surface temperature of less than 4,000 K. Did you know?
SubcategoriesTo display all subcategories click on the ►
Selected biography - Photo credit: Unknown artist, uploaded by User:Salvatore Ingala
Claudius Ptolemaeus (Greek: Κλαύδιος Πτολεμαῖος Klaúdios Ptolemaîos; c. AD 90 – c. 168), known in English as Ptolemy /ˈtɒləmɪ/, was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer and a poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the Thebaid. He died in Alexandria around AD 168. Ptolemy was the author of several scientific treatises, at least three of which were of continuing importance to later Islamic and European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the Almagest (in Greek, Ἡ Μεγάλη Σύνταξις, "The Great Treatise", originally Μαθηματικὴ Σύνταξις, "Mathematical Treatise"). The second is the Geography, which is a thorough discussion of the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise known sometimes in Greek as the Apotelesmatika (Ἀποτελεσματικά), more commonly in Greek as the Tetrabiblos (Τετράβιβλος, "Four Books"), and in Latin as the Quadripartitum (or "Four Books") in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. In Almagest, considered to be one of the most influential scientific texts of all time, Ptolemy presented his astronomical models in convenient tables, which could be used to compute the future or past position of the planets. The Almagest also contains a star catalogue, which is an appropriated version of a catalogue created by Hipparchus. His Planetary Hypotheses went beyond the mathematical model of the Almagest to present a physical realization of the universe as a set of nested spheres. TopicsThings to do
Related portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |