Portal:Cornwall
 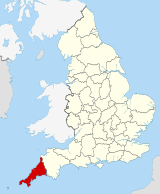 Cornwall (/ˈkɔːrnwɔːl, -wəl/; Cornish: Kernow; Cornish pronunciation: [ˈkɛrnɔʊ]; or [ˈkɛrnɔ]) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised by Cornish and Celtic political groups as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest settlement is Falmouth, and the county town is the city of Truro. The county is rural, with an area of 1,375 square miles (3,562 km2) and population of 568,210. After Falmouth (23,061), the largest settlements are Penzance, Newquay, St Austell, and Truro. For local government purposes most of Cornwall is a unitary authority area, with the Isles of Scilly having a unique local authority. The Cornish nationalist movement disputes the constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is the westernmost part of the South West Peninsula. Its coastline is characterised by steep cliffs and, to the south, several rias, including those at the mouths of the rivers Fal and Fowey. It includes the southernmost point on Great Britain, Lizard Point, and forms a large part of the Cornwall National Landscape. The national landscape also includes Bodmin Moor, an upland outcrop of the Cornubian batholith granite formation. The county contains many short rivers; the longest is the Tamar, which forms the border with Devon. (Full article...) Selected article A bal maiden, from the Cornish language bal, a mine, and the English "maiden", a young or unmarried woman, was a female manual labourer working in the mining industries of Cornwall and western Devon, at the south-western extremity of Great Britain. The term has been in use since at least the early 18th century. At least 55,000 women and girls worked as bal maidens, and the actual number is likely to have been much higher. While women worked in coal mines elsewhere in Britain, either on the surface or underground, bal maidens worked only on the surface. It is likely that Cornish women had worked in metal mining since antiquity, but the first records of female mine workers date from the 13th century. After the Black Death in the 14th century, mining declined, and no records of female workers have been found from then until the late 17th century. Industrial improvements, the end of Crown control of metal mines, and rising demand for raw materials caused a boom in Cornish mining in the late 17th and early 18th centuries. Increasing numbers of women and girls were recruited to the mines from about 1720, processing ore sent up by the male miners underground. The discovery of cheaper sources of copper in North Wales in the 1770s triggered a crash in the copper price, and many mines closed. As the Industrial Revolution began in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, the Welsh metal mines declined and mining in Cornwall and Devon became viable once more. Women and girls were recruited in large numbers for work in ore processing. Women and children accounted for up to half the workers in the area's copper mines. Although machinery was capable of performing much of the work done by bal maidens, the industry grew so quickly that the number of women and girls working grew steadily even though their numbers fell as a proportion of the workforce to 15–20% by 1850. At the peak of the Cornish mining boom, in around 1860, at least 6,000 bal maidens were working at the region's mines; the actual number is likely to have been much higher. While it was not unusual for girls to become bal maidens at the age of six and to work into old age, they generally began at around age 10 or 11 and left work once they married. From the 1860s, Cornish mines faced competition from cheap metal imports, and legislation introduced in the 1870s limited the use of child labour. The Cornish mining system went into terminal decline, leading to a collapse of the local economy and mass emigration both overseas and to other parts of the United Kingdom. In 1891 the number of bal maidens had fallen to half its peak, and by the outbreak of the First World War in 1914 very few remained in employment. In 1921 Dolcoath mine, the last employer of bal maidens, ceased operations, bringing the tradition to an end. Other than women recruited for ore processing at Geevor as a result of labour shortages during the Second World War, and a very few female workers after the Sex Discrimination Act 1975 banned the practice of recruiting only male mineworkers, women never again performed manual labour in Cornish mines. The last surviving bal maiden died in 1968, and with the closure of South Crofty tin mine in 1998, Cornish metals mining came to an end. (Full article...)Selected biography
Did you know?
Selected quoteSelected picture
General imagesThe following are images from various Cornwall-related articles on Wikipedia.
WikiProjects
Related portalsTopicsHistory
Geography
Politics
Economy and demographics
Culture
SubcategoriesRecognised content
Featured articlesMain page featured articlesFeatured listsGood articles
Former good articlesIn the News articlesThings you can do'
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikipedia in CornishDiscover Wikipedia using portals
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



































































