Portal:Caribbean
| Main Portal page | Indices | Projects |
 |
 |

| |
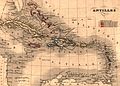
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/ KARR-ih-BEE-ən, kə-RIB-ee-ən, locally /ˈkærɪbiːæn/ KARR-ih-bee-an; Spanish: el Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Dutch: de Caraïben) is a subregion of the Americas that includes the Caribbean Sea and its islands, some of which are surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some of which border both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean; the nearby coastal areas on the mainland are sometimes also included in the region. The region is south-east of the Gulf of Mexico and Northern America, east of Central America, and north of South America.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs, and cays. Island arcs delineate the northern and eastern edges of the Caribbean Sea: the Greater Antilles in the north and the Lesser Antilles, which includes the Leeward Antilles, in the east and south. The nearby Lucayan Archipelago, comprising The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, is considered to be a part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. All the islands in the Antilles plus the Lucayan Archipelago form the West Indies, which is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean. On the mainland, Belize, the eastern and northern coasts of Central and South American countries such as the Bay Islands Department of Honduras, the North and South Caribbean Autonomous Regions of Nicaragua, the Limón Province of Costa Rica, and the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina of Colombia are also considered culturally Caribbean. French Guiana, Guyana, Panama, and Suriname are often included as parts of the Caribbean due to their political and cultural ties with the region.
Geopolitically, the islands of the Caribbean are often regarded as a subregion of North America, though sometimes they are included in Middle America or left as a subregion of their own; alternately, the term "Caribbean" may have the intended exclusion, or even unintentional inclusion, as part of Latin America. Generally the Caribbean area is organized into 33 political entities, including 13 sovereign states, 12 dependencies, historical disputed territories have existed, and seven other overseas territories. From 15 December 1954 to 10 October 2010, there was a territory known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five islands, all of which were Dutch dependencies. From 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the British West Indies Federation composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies. (Full article...)
Anarchism as a social movement in Cuba held great influence with the working classes during the 19th and early 20th century. The movement was particularly strong following the abolition of slavery in 1886, until it was repressed first in 1925 by President Gerardo Machado, and more thoroughly by Fidel Castro's Marxist–Leninist government following the Cuban Revolution in the late 1950s. Cuban anarchism mainly took the form of anarcho-collectivism based on the works of Mikhail Bakunin and, later, anarcho-syndicalism. The Latin American labor movement, and by extension the Cuban labor movement, was at first more influenced by anarchism than Marxism. (Full article...)
Selected geography article -

Dominica (locally /ˌdɒmɪˈniːkə/ dom-in-EE-kə; UK: US: /ˌdɒmɪˈniːkə/ or /dəˈmɪnɪkə/ ⓘ; Dominican Creole French: Dominik; Kalinago: Waitukubuli), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. It is part of the Windward Islands chain in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. Dominica's closest neighbours are two constituent territories of the European Union, the overseas departments of France, Guadeloupe to the northwest and Martinique to the south-southeast. Dominica comprises a land area of 750 km2 (290 sq mi), and the highest point is Morne Diablotins, at 1,447 m (4,747 ft) in elevation. The population was 71,293 at the 2011 census.
The island was settled by the Arawak arriving from South America in the fifth century. The Kalinago displaced the Arawak by the 15th century. Christopher Columbus is said to have passed the island on Sunday, 3 November 1493. It was later colonised by Europeans, predominantly by the French from the 1690s to 1763. The French imported enslaved people from West Africa to Dominica to work on coffee plantations. Great Britain took possession in 1763 after the Seven Years' War, and it gradually established English as its official language. The island gained independence as a republic in 1978. (Full article...)Selected fare or cuisine -
Caribbean Chinese cuisine is a style of food resulting from a fusion of Chinese and West Indian cuisines. The Chinese influence is predominantly Cantonese, the main source of Chinese immigrants to the West Indies. West Indian food is itself a mixture of African, British, Indian, Spanish, French, Portuguese, Middle Eastern, Afghan and cooking styles.
Although a long-favoured cuisine in West Indian restaurants and Chinese-Caribbean households, it is only recently that an increase in number of Caribbean–Chinese restaurants has occurred in Canada and the United States. These are more often than not “Guyanese restaurants” owing to that country's particular historical connection to Chinese immigration, although signs may also claim “Caribbean Chinese food,” “West Indian and Chinese cuisine”, or variations thereof. (Full article...)Did you know? -

- ...that Isla Margarita (pictured), the largest Caribbean island of the Nueva Esparta State in Venezuela, was seized by Lope de Aguirre, a notoriously violent and rebellious conquistador in 1561? And that he held the islanders in a grip of terror until he returned to the mainland in an attempt to take Panama from the Spanish crown?
- ...that Narciso López fled Cuba for New York City in 1848 after a failed attempt to create a revolt among Cuban planters, and attempted three times to raise filibuster expeditions to invade Cuba from the U.S.?
- ...that the Universidad Autónoma de Santo Domingo is a public university in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic? And that it is the oldest institution of higher education in the western hemisphere?
Related portals
Wikiproject
The music of the Lesser Antilles encompasses the music of this chain of small islands making up the eastern and southern portion of the West Indies. Lesser Antillean music is part of the broader category of Caribbean music; much of the folk and popular music is also a part of the Afro-American musical complex, being a mixture of African, European and indigenous American elements. The Lesser Antilles' musical cultures are largely based on the music of African slaves brought by European traders and colonizers. The African musical elements are a hybrid of instruments and styles from numerous West African tribes, while the European slaveholders added their own musics into the mix, as did immigrants from India. In many ways, the Lesser Antilles can be musically divided based on which nation colonized them.
The former British colonies include Trinidad and Tobago, whose calypso style is an especially potent part of the music of the other former British colonies, which also share traditions like the Big Drum dance. The French islands of Martinique and Guadeloupe share the popular zouk style and have also had extensive musical contact with the music of Haiti, itself once a French colony though not part of the Lesser Antilles. The Dutch colonies of Curaçao, Bonaire and Aruba share the combined rhythm popular style. The islands also share a passion for kaseko, a genre of Surinamese music; Suriname and its neighbors Guyana and French Guiana share folk and popular styles that are connected enough to the Antilles and other Caribbean islands that both countries are studied in the broader context of Antillean or Caribbean music. (Full article...)Selected image -

Interior of Cathedral Primada in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic.
Selected music -

Rumba is a secular genre of Cuban music involving dance, percussion, and song. It originated in the northern regions of Cuba, mainly in urban Havana and Matanzas, during the late 19th century. It is based on African music and dance traditions, namely Abakuá and yuka, as well as the Spanish-based coros de clave. According to Argeliers León, rumba is one of the major "genre complexes" of Cuban music, and the term rumba complex is now commonly used by musicologists. This complex encompasses the three traditional forms of rumba (yambú, guaguancó and columbia), as well as their contemporary derivatives and other minor styles.
Traditionally performed by poor workers of African descent in streets and solares (courtyards), rumba remains one of Cuba's most characteristic forms of music and dance. Vocal improvisation, elaborate dancing and polyrhythmic drumming are the key components of all rumba styles. Cajones (wooden boxes) were used as drums until the early 20th century, when they were replaced by tumbadoras (conga drums). During the genre's recorded history, which began in the 1940s, there have been numerous successful rumba bands such as Los Papines, Los Muñequitos de Matanzas, Clave y Guaguancó, AfroCuba de Matanzas and Yoruba Andabo. (Full article...)General images
Caribbean topics
Categories
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-05-14 20:03 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Catherine Basie (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dbiunno (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-14, score: 16
- William Alexander Ancrum (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ceballenger (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-14, score: 16
- Alfredo Rego (general) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-05-14, score: 16
- Paul Casamajor (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ysh.cabana (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-13, score: 24
- Mary Adella Wolcott (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gamaliel (talk · contribs · new pages (46)) started on 2024-05-13, score: 16
- Donald Rhodd (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2024-05-13, score: 16
- Louis-Pantaléon de Noé (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shellypls (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-05-13, score: 32
- Güijes (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Caireau (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-13, score: 24
- Orthosia scoparia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FloridaArmy (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2024-05-13, score: 112
- Evan Harmeling (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CNMall41 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-05-13, score: 24
- Booby Island (Saint Kitts and Nevis) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thebiguglyalien (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-13, score: 75
- Tafraout Group (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yewtharaptor (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-12, score: 24
- Major divisions of Antigua and Barbuda (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Funandtrvl (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-12, score: 32
- Baddies season 5 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WikiRedactor (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 24
- 2024 Nor.Ca. Men's Handball Championship (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kante4 (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Rosendo Collazo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-05-12, score: 16
- Margaret G. Bradbury (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Quetzal1964 (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-05-12, score: 16
- Leah Anderson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (112)) started on 2024-05-12, score: 32
- 2024 Girls' U17 Pan-American Volleyball Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thiago89 (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-05-12, score: 16
- 2025 CONCACAF Champions Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GolazoGolazo1234 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-12, score: 16
- Kostiantyn Kostenevych (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Oberhof (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-12, score: 16
- Pedro Vives (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (57)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 16
- Ramiro Mora Romero (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shrug02 (talk · contribs · new pages (17)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 16
- 2006 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 16
- Bangladeshi cricket team in the West Indies in 2024–25 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Goodknowme (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 32
- Rose Powhatan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Daniellemuniz (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- 2004 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 16
- Dominica International Airport (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by LivinAWestLife (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 16
- Caritas Latin America and Caribbean (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bdx (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 67
- Samuel Ogazi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (112)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 16
- Savi Naipaul Akal (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lewisguile (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 51
- Stateside Virgin Islanders (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Avengers350 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-11, score: 123
- 2000 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- Effort of scientific researchers in Haiti (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Delpolocovy (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-04-29, score: 16
- Caritas Colombia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bdx (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- 1996 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- 1994 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- La Durango (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Floppykart (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- Juan Delgado (baroque painter) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sonero9 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- 1992 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- 1990 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- Weather of 2001 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MemeGod27 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- Nicholson Ducreay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sammielh (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 24
- List of United States governors born outside the United States (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hemant Dabral (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 24
- Noche de Pasión (song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DominicanWikiEdit1996 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- Krishnamachari Srikkanth (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 106.222.196.102 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- 1986 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- Los Kakukomicos (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeanetteMartin (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- 1982 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-10, score: 16
- 1977 United States Virgin Islands Constitutional Convention election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yilku1 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 16
- La Dame Blanche (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Qcne (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 24
- Quiina guianensis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CycoMa1 (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 16
- George Allan Madden (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WikiOriginal-9 (talk · contribs · new pages (238)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 12
- Christian Lilly (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WikiOriginal-9 (talk · contribs · new pages (238)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 56
- De Carolina (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by آرمین هویدایی (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 16
- Samuel Raymond Jarvis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Waggers (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 32
- 2024–25 CONCACAF Nations League C (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thiago89 (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 56
- Conquering Lion (album) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GanzKnusper (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 16
- Kate Wilmott (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Goodknowme (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 32
- Tripsacum lanceolatum (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WelwitschiaTokarev (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 16
- Inauguration of Andrés Pastrana (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AlexExpensive (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-05-09, score: 16
- Charles P. Buchanan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dougiethelass (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 16
- List of ambassadors of Spain to the Dominican Republic (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 24
- Rusking Pimentel (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Caddygypsy (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 32
- Adam Bednarik (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yearingout (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- Adivino (song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Floppykart (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 16
- St. Albert the Great Priory (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Qcne (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 16
- Robert Grant (Royal Engineers) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WikiOriginal-9 (talk · contribs · new pages (238)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 16
- Bby Boo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Goshiy (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 16
- Lists of Italian Americans (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Omnis Scientia (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 24
- Arthur William Mahaffy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Xegma (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-08, score: 16
- NSGB (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AllTheUsernamesAreInUse (talk · contribs · new pages (127)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- Elsie Etheart (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bookworm-ce (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- Pineapple mania (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Viriditas (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 24
- Tyler Ferguson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stonecold415 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 12
- Pedro José de Zulueta, 2nd Count of Torre Díaz (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DACC23 (talk · contribs · new pages (29)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- Latin American Federation of Journalists (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bookworm-ce (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 24
- Casting the Atlantic (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cantillismo (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- List of elections in 2026 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yoblyblob (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- Museo de las Américas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Blapgar (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- 2025 Belizean general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yoblyblob (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 19
- Cuban Boxing Federation (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- Suriname national futsal team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HitroMilanese (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 56
- Giraldo Cordova Cardin International Boxing Tournament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- Plaza del Atlántico (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ruud Buitelaar (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 24
- Brunache (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Zigzig20s (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-05-07, score: 16
- List of IMAX venues with 15/70 or laser projectors (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Travelling nomad1 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 24
- List of Phi Delta Epsilon chapters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jax MN (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- The Firing Squad (2024 film) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by The Film Creator (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- Carmen Vazquez Rivera (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Atlasunivers (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 24
- C, XOXO (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nikolasivy13 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- Deaths in April 2024 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rusted AutoParts (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 24
- Baticano (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Floppykart (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- Lyndon Campos (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pietaster (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- Palais de la Belle Rivière (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ipflo (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- 2024 World Athletics Relays – Women's 4 × 100 metres relay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Habst (talk · contribs · new pages (128)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- 2024 World Athletics Relays – Women's 4 × 400 metres relay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jennypedia (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- 2024 World Athletics Relays – Men's 4 × 400 metres relay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Habst (talk · contribs · new pages (128)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- BeyGood (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Newpicarchive (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- 1995 Choco earthquake (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by LeSwiss1886 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- Randy Rodríguez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stonecold415 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-06, score: 16
- Results of the 2012 Ukrainian parliamentary election in the foreign electoral district (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lastjourneyman. (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 24
- Latin Caribbean (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GreekApple123 (talk · contribs · new pages (45)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 107
- Dorsainvil (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Edwardx (talk · contribs · new pages (82)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- Charles Oscar Etienne (Chaloska) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Alyssa.Bustos (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 44
- 2024 World Athletics Relays – Mixed 4 × 400 metres relay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jennypedia (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- Vancouver Knights (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sagar Singh 9 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- Harry M. Locke (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jeffrey Beall (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- Dagoberto (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GiantSnowman (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- Adi Oasis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EmphaXVI (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 24
- Bryan Ramos (baseball) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pozzi.c (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- 2024 World Athletics Relays – Men's 4 × 100 metres relay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Alibene567 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 32
- Luis Enrique Patterson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Betterthanbutter (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 32
- Cardamine occulta (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Abductive (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- Civil Service College (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ΚΚ ΙΝ ΗΚ (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-05, score: 16
- Alberto Bosch y Fustegueras (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (57)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Edelweiss Capital Group Limited (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Limbo.J (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Carolina Armenteros (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Trakking (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Lejos del Cielo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by آرمین هویدایی (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 24
- Costa Rica–Panama relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rkt2312 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Anna Stembridge (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Djln19 (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Costa Rica–Nicaragua relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rkt2312 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Honduras–Nicaragua relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rkt2312 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Claire Jimenez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ruth Bader Yinzburg (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Independence Day (Haiti) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheBrowniess (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- El Salvador–Honduras relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rkt2312 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- El Salvador–Guatemala relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rkt2312 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Roger Shakespear (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HangingSwordAlley (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 32
- Guatemala–Honduras relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rkt2312 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Eric Zolov (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Reykcultura7193 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 24
- Embassy of Haiti, Taipei (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Zinderboff (talk · contribs · new pages (17)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- List of Danish colonial trading posts and settlements (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tinkaer1991 (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 24
- Deaths in February 1987 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mill 1 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 24
- Wilfredo Ferrer (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pietaster (talk · contribs · new pages (22)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 27
- Deaths in March 1987 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mill 1 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 24
- Carlos Rivera (politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Unknown Temptation (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Miss Grand United States Virgin Islands 2024 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thomson Walt (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 24
- Beryl Piccolantonio (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ktkvtsh (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-04, score: 16
- Alfonso Ardura (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (57)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- 1940 United States Virgin Islands general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Longestview (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- Deaths in April 1987 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mill 1 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 24
- Deaths in June 1987 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mill 1 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 48
- Henry Klein (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GiantSnowman (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- Helen Jane Gladstone (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GnocchiFan (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2024-04-29, score: 16
- Pancho Mansfield (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jmondry (talk · contribs · new pages (0)) started on 2024-04-23, score: 32
- Bayron (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Duckmather (talk · contribs · new pages (102)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- Rojé Stona (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (112)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- 2004 North Carolina Democratic presidential caucuses (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SphealKent (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- Census in Jamaica (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jeffrolland (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- Mister Venezuela 1998 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mauriziok (talk · contribs · new pages (49)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 20
- Pedro Pagés (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robertsky (talk · contribs · new pages (44)) started on 2024-05-03, score: 16
- Princesa (song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DominicanWikiEdit1996 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- John Edwards Caldwell (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DMVHistorian (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- List of ambassadors and high commissioners to New Zealand (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bouzinac (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- SS Nyassa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Motacilla (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 32
- Fiorinia phantasma (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bernhard Zelazny (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- Admetula formosa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JoJan (talk · contribs · new pages (39)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- Tharan Yaub Yuhanim (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yusuf Asar Yathar (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- Eugenio Martínez Thedy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fadesga (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- Samuel Joyce Thomas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by C411978 (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- Dasvibes (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ubs45ya (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- Peter Bown (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Solde (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-02, score: 16
- Antonio Alonso (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (57)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- 2024 CONCACAF Champions Cup final (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 2pou (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Zootopia 2 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 2604:3D09:7A7C:B200:F1BE:83FF:8531:8019 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- A. A. Priestley's cricket team in the West Indies in 1896–97 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Batagur baska (talk · contribs · new pages (55)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 56
- List of Phi Kappa Phi chapters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-04-30, score: 16
- Rochelle Neil (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (112)) started on 2024-04-28, score: 16
- Solo Te Amo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DominicanWikiEdit1996 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Triste Verano (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Floppykart (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Fritz Bélizaire (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SashiRolls (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Jany Martínez-Ward (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Seenery (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- South Africa at the 2024 ICC Men's T20 World Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wowlastic10 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Afghanistan at the 2024 ICC Men's T20 World Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wowlastic10 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 24
- England at the 2024 ICC Men's T20 World Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wowlastic10 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 24
- Ecuador women's national under-17 football team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SunsetRunner77 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Luis Armelio Garcia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Das osmnezz (talk · contribs · new pages (55)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 56
- Caritas Mexico (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bdx (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Scarlin Hernandez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Theroadislong (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- List of Ethical Culture Fieldston School alumni (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Melchior2006 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Australia at the 2024 ICC Men's T20 World Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wowlastic10 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 32
- Disruption of the water cycle in Haiti (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Delpolocovy (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 24
- Anestesiada (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DominicanWikiEdit1996 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-01, score: 16
- Timeline of the 1993 Atlantic hurricane season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dylan620 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-04-30, score: 96
- MV Commodore Clipper (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 51.7.191.117 (talk · contribs · new pages (0)) started on 2024-04-29, score: 16
- Nhlakanipho MT Gumede (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GumedeNhl (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-04-30, score: 16
- Nhlakanipho Mbongeni Theobald Gumede (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GumedeNhl (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-04-30, score: 16
- Bicycles on stamps (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GreatStellatedDodecahedron (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-04-30, score: 16
- Epsilon Telecommunications Limited (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bager Drukit (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-04-30, score: 16
- Doryan Rodríguez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (112)) started on 2024-04-30, score: 16
- Orelvis Martínez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kline (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-04-30, score: 16
- Widens Pkolo Dorsainville (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pkolo69d (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-04-18, score: 16
- WJ Kruys (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CroiXXX (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-04-26, score: 16
- Necesito de Ti (song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DominicanWikiEdit1996 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-04-25, score: 16
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Shortcuts to this page: Portal:West Indies • P:CARIB Purge server cache