Portal:Madagascar
The Madagascar Portal
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country comprising the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's fourth largest island, the second-largest island country and the 44th largest country in the world. Its capital and largest city is Antananarivo. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from Africa during the Early Jurassic, around 180 million years ago, and split from the Indian subcontinent around 90 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation; consequently, it is a biodiversity hotspot and one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries, with over 90% of wildlife being endemic. The island has a subtropical to tropical maritime climate. Madagascar was first settled during or before the mid-first millennium AD by Austronesian peoples, presumably arriving on outrigger canoes from present-day Indonesia. These were joined around the ninth century AD by Bantu migrants crossing the Mozambique Channel from East Africa. Other groups continued to settle on Madagascar over time, each one making lasting contributions to Malagasy cultural life. Consequently, there are 18 or more classified peoples of Madagascar, the most numerous being the Merina of the central highlands. Until the late 18th century, the island of Madagascar was ruled by a fragmented assortment of shifting sociopolitical alliances. Beginning in the early 19th century, most of it was united and ruled as the Kingdom of Madagascar by a series of Merina nobles. The monarchy was ended in 1897 by the annexation by France, from which Madagascar gained independence in 1960. The country has since undergone four major constitutional periods, termed republics, and has been governed as a constitutional democracy since 1992. Following a political crisis and military coup in 2009, Madagascar underwent a protracted transition towards its fourth and current republic, with constitutional governance being restored in January 2014. (Full article...) This is a Featured article, which represents some of the best content on English Wikipedia..
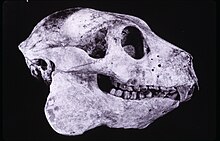
Babakotia is an extinct genus of medium-sized lemur, or strepsirrhine primate, from Madagascar that contains a single species, Babakotia radofilai. Together with Palaeopropithecus, Archaeoindris, and Mesopropithecus, it forms the family Palaeopropithecidae, commonly known as the sloth lemurs. The name Babakotia comes from the Malagasy name for the indri, babakoto, to which it and all other sloth lemurs are closely related. Due to its mix of morphological traits that show intermediate stages between the slow-moving smaller sloth lemurs and the suspensory large sloth lemurs, it has helped determine the relationship between both groups and the closely related and extinct monkey lemurs. Babakotia radofilai and all other sloth lemurs share many traits with living sloths, demonstrating convergent evolution. It had long forearms, curved digits, and highly mobile hip and ankle joints. Its skull was more heavily built than that of indriids, but not as much as in the larger sloth lemurs. Its dentition is similar to that of all other indriids and sloth lemurs. It lived in the northern part of Madagascar and shared its range with at least two other sloth lemur species, Palaeopropithecus ingens and Mesopropithecus dolichobrachion. Babakotia radofilai was primarily a leaf-eater (folivore), though it also ate fruit and hard seeds. It is known only from subfossil remains and may have died out shortly after the arrival of humans on the island, but not enough radiocarbon dating has been done with this species to know for certain. (Full article...)Selected article - Salegy (Malagasy pronunciation: [ˈsaleɡʲ]) is a popular music genre from Madagascar. Originating as a Sub-Saharan African folk music style in the northwestern coastal areas of Madagascar, modern salegy is the genre of Malagasy music that has gained the widest recognition and commercial popularity in the international market. Its sound is considered emblematic of the island. Eusèbe Jaojoby, a Sakalava singer from Anboahangibe , was a key originator of the style and is widely considered the "King of Salegy". The contemporary, electrified form of popular salegy originated from traditional acoustic roots in northwestern Madagascar around Mahajanga and Antsiranana in the 1950s. It has been popularized by originators like Jaojoby and relative newcomers such as Ninie Doniah, Vaiavy Chila and Dr. J.B. and the Jaguars. The style is funky and energetic, dominated by ringing electric guitars, real or synthesized accordion, and call-and-response polyphonic vocals, propelled by heavy electric bass and a driving percussion section typically including a drum kit, djembe and shakers. The syncopated, polyrhythmic beat of salegy is rapid (typically around 290BPM) and features a distinctive percussion pattern performed on a Western drum kit in 68 or 12 4 time with accents on the 3rd or 7th beat. The melody and harmonies are often in the A minor key and feature beautiful high-life electric guitar and synthesized accordion lines. The sound of salegy can be heard at night clubs, cabarets, parties and dance floors across the island. (Full article...) This is a Good article, an article that meets a core set of high editorial standards.
 Gerp's mouse lemur (Microcebus gerpi) is a species of mouse lemur known only from the Sahafina Forest in eastern Madagascar, near Mantadia National Park. Its discovery was announced in 2012 by a German and Malagasy research team. The Sahafina Forest had not been studied until 2008 and 2009, when Groupe d'Étude et de Recherche sur les Primates de Madagascar (GERP)—a Malagasy-based research and conservation group for which the lemur is named—inventoried the forest's lemurs. Based on genetic studies, measurements, and photos, the research team confirmed the Gerp's mouse lemur was an undescribed species, distinct from Goodman's mouse lemur, which is found 58-kilometre (36 mi) away. Gerp's mouse lemur is significantly larger, weighing on average 68-gram (2.4 oz), compared to Goodman's mouse lemur, which weighs about 44 g (1.6 oz). Jolly's mouse lemur, which is its closest relative and a neighbor to the south, is comparably larger, but differs in tail length and genetics. (Full article...)General images -The following are images from various Madagascar-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected panoramaLandscape near Fianarantsoa, Madagascar.
TopicsCategoriesSelected pictureAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals | |||