Portal:Texas
The Texas Portal
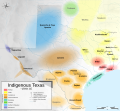
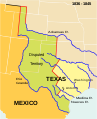
Texas (/ˈtɛksəs/ TEK-səss, locally also /ˈtɛksɪz/ TEK-siz; Spanish: Texas or Tejas, pronounced [ˈtexas]) is the most populous state in the South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest. Texas has a coastline on the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Covering 268,596 square miles (695,660 km2), and with over 30 million residents as of 2023, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both area and population. Texas is nicknamed the Lone Star State for its former status as an independent republic. The Lone Star can be found on the Texas state flag and the Texas state seal. Spain was the first European country to claim and control the area of Texas. Following a short-lived colony controlled by France, Mexico controlled the territory until 1836 when Texas won its independence, becoming the Republic of Texas. In 1845, Texas joined the United States as the 28th state. The state's annexation set off a chain of events that led to the Mexican–American War in 1846. Following victory by the United States, Texas remained a slave state until the American Civil War, when it declared its secession from the Union in early 1861 before officially joining the Confederate States of America on March 2. After the Civil War and the restoration of its representation in the federal government, Texas entered a long period of economic stagnation. Historically, four major industries shaped the Texas economy prior to World War II: cattle and bison, cotton, timber, and oil. Before and after the Civil War, the cattle industry—which Texas came to dominate—was a major economic driver and created the traditional image of the Texas cowboy. In the later 19th century, cotton and lumber grew to be major industries as the cattle industry became less lucrative. Ultimately, the discovery of major petroleum deposits (Spindletop in particular) initiated an economic boom that became the driving force behind the economy for much of the 20th century. Texas developed a diversified economy and high tech industry during the mid-20th century. , it has the most Fortune 500 company headquarters (53) in the United States. With a growing base of industry, the state leads in many industries, including tourism, agriculture, petrochemicals, energy, computers and electronics, aerospace, and biomedical sciences. Texas has led the U.S. in state export revenue since 2002 and has the second-highest gross state product. (Full article...) Selected article -The Texas Revolution (October 2, 1835 – April 21, 1836) was a rebellion of colonists from the United States and Tejanos (Hispanic Texans) against the centralist government of Mexico in the Mexican state of Coahuila y Tejas. Although the uprising was part of a larger one, the Mexican Federalist War, that included other provinces opposed to the regime of President Antonio López de Santa Anna, the Mexican government believed the United States had instigated the Texas insurrection with the goal of annexation. The Mexican Congress passed the Tornel Decree, declaring that any foreigners fighting against Mexican troops "will be deemed pirates and dealt with as such, being citizens of no nation presently at war with the Republic and fighting under no recognized flag". Only the province of Texas succeeded in breaking with Mexico, establishing the Republic of Texas. It was eventually annexed by the United States. The revolution began in October 1835, after a decade of political and cultural clashes between the Mexican government and the increasingly large population of Anglo-American settlers in Texas. The Mexican government had become increasingly centralized and the rights of its citizens had become increasingly curtailed, particularly regarding immigration from the United States. Mexico had officially abolished slavery in Texas in 1829, and the desire of Anglo Texans to maintain the institution of chattel slavery in Texas was also a major cause of secession. Colonists and Tejanos disagreed on whether the ultimate goal was independence or a return to the Mexican Constitution of 1824. While delegates at the Consultation (provisional government) debated the war's motives, Texians and a flood of volunteers from the United States defeated the small garrisons of Mexican soldiers by mid-December 1835. The Consultation declined to declare independence and installed an interim government, whose infighting led to political paralysis and a dearth of effective governance in Texas. An ill-conceived proposal to invade Matamoros siphoned much-needed volunteers and provisions from the fledgling Texian Army. In March 1836, a second political convention declared independence and appointed leadership for the new Republic of Texas. (Full article...)Selected biography - Texas news
Wikinews Texas portal
ListsState symbols
Texas topicsSelected image Credit: User:Ichabod Dr Pepper Museum in Waco, Texas. Damage inflicted by the 1953 Waco Tornado can be clearly seen in the newer, lighter bricks along the top-front quarter of the building. Cities -El Paso (/ɛl ˈpæsoʊ/; Spanish: [el ˈpaso]; lit. 'the pass' or 'the step') is a city in and the county seat of El Paso County, Texas, United States. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 22nd-most populous city in the U.S., the most populous city in West Texas, and the sixth-most populous city in Texas. Its metropolitan statistical area covers all of El Paso and Hudspeth counties in Texas, and had a population of 868,859 in 2020. El Paso stands on the Rio Grande across the Mexico–United States border from Ciudad Juárez, the most populous city in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. The Las Cruces area, in the neighboring U.S. state of New Mexico, has a population of 219,561. On the U.S. side, the El Paso metropolitan area forms part of the larger El Paso–Las Cruces combined statistical area, which has a population of 1,098,541. These three cities form a combined international metropolitan area sometimes referred to as the Paso del Norte or the Borderplex. The region of 2.7 million people constitutes the largest bilingual and binational workforce in the Western Hemisphere. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Texas-related articles on Wikipedia.
CategoriesSelect [►] to view subcategories
Related pages
Attractions
 Things you can doAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
SourcesMore portals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||